The female reproductive system is the complex of organs and anatomical structures which in women have the purpose of ensuring the mechanism of reproduction. The pathologies of the female genital tract affect the different ages of woman's life, ranging from puberty to fertile age, to the time of pregnancy up to premenopause and overt menopause.

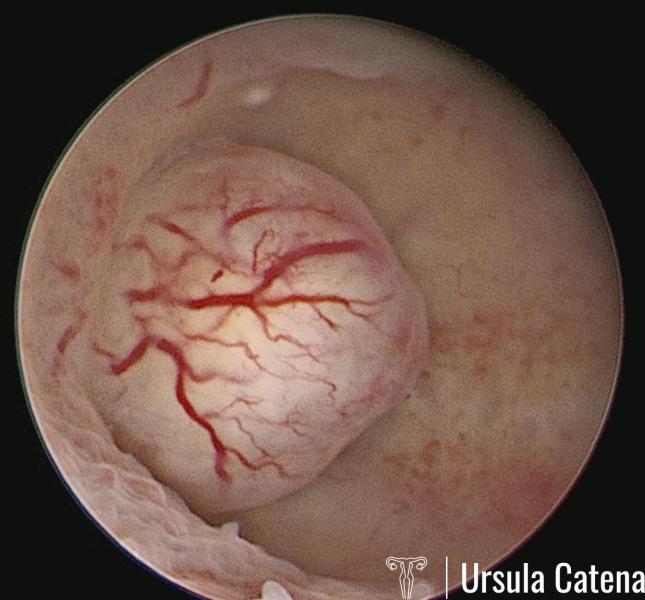
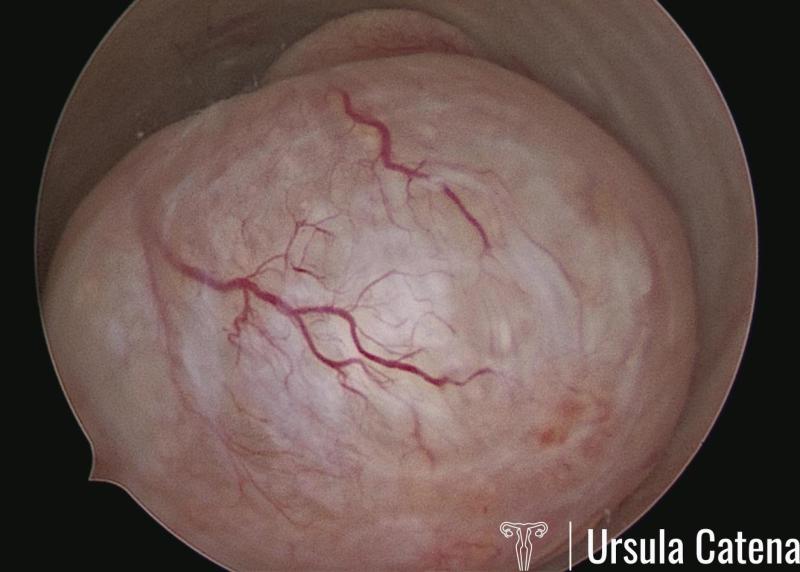
Uterine fibroids (also known as leiomyomas or myomas) consisting of smooth muscle and a variable amount of connective tissue, are the most common benign solid tumors of the female genital tract, affecting 20–25% of women of reproductive age.
The myoma initially grows inside the myometrium and then tends, displacing the surrounding myometrial fibers, to move towards areas of less resistance: the abdominal cavity or the uterine cavity.
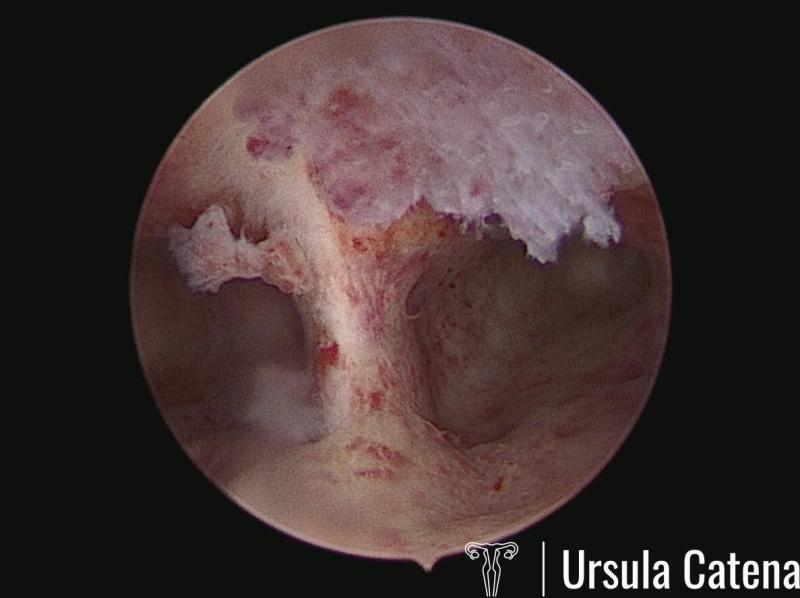
Endometrial polyps are focal benign neoformations of the endometrial mucosa consisting of a stromal axis lined with cylindrical epithelium containing a variable amount of blood vessels.
About 20% of women are affected, particularly in the fifth decade of life.
Numerous causes associated with the appearance of endometrial polyps have been hypothesized; they include genetic and hereditary factors, inflammatory factors, endocrine factors, iatrogenic factors (unbalanced estrogen therapy, tamoxifen therapy for breast cancer).
LCongenital uterine malformations (CUM) are deviations from normal anatomy resulting from incorrect embryological development. 5.5% of women are affected if we consider the general population, 8.0% of infertile women, 13.3% if we consider women with a history of spontaneous abortions and 24.5% considering those with previous miscarriages and infertility.
Endometrial Carcinoma represents about 5% of female cancers worldwide. In 2022, there were 420,368 new cases of endometrial carcinoma recorded globally. Among these patients, about 3% were aged between 15 and 44 years (Globocan 2022)
From January 2021 to December 2023, 100 patients with an initial diagnosis of endometrial cancer and atypical complex hyperplasia (39 endometrial cancer and 61 atypical complex hyperplasia) were conservatively treated by Dr. Catena at the CLASS Hysteroscopy center of the Policlinico Universitario Agostino Gemelli IRCCS of Rome..


Residual products of conception (RPOC) can occur after an early or late abortion, after an early or late pregnancy termination (TOP), or after a vaginal delivery or caesarean section. This event appears to complicate approximately 1% of full-term pregnancies. At the CLASS Hysteroscopy Center, it is possible to treat placental remnants with innovative techniques. First of all, hysteroscopy allows to directly visualize the uterine cavity and, therefore, to remove the pathology under vision by removing it completely in a safe and effective way.


